1 Introduction:
In the last
chapter we have studied about the basic steps to start with in order to work in
oracle apps or EBS. So as in our check list we have covered two steps i.e
Step 1: Creation
of user
Step 2: Creation
of responsibility and assigning them to the user and testing by logging.
In this chapter
we will take the next step i.e. defining of 4Cs which are
1st C:
COA
2nd C:
Currency
3rd C:
Calendar
4th C:
SLA (This being a typical and business level setup we will be taking it up
separately.)
2
Explanation
But before
starting with the 4c we would like to briefly discuss with the multi-org
structure which is as follows
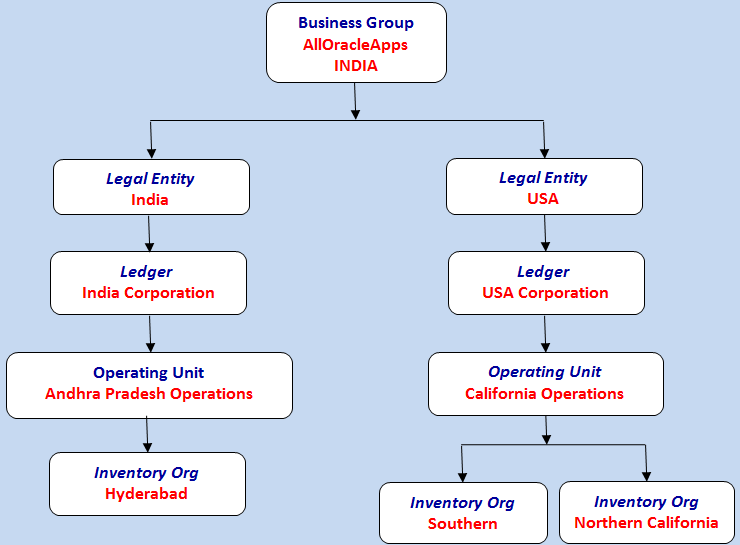
Now in the above
structure we can see that at the top we have the business group followed by
legal entity followed by ledger and then the operating unit and inventory org.
In the above
structure we have ledger which is a new concept in R12. In 11i we had set of
books and in R12 we have ledger which comprises of four things i.e. 4 Cs
·
Calendar
·
Currency
·
COA i.e. Chart of Accounts or Accounting
Flexfieds
·
SLA i.e. Sub-ledger Accounting
3 List of basic setups
Although everything will not be discussed in
this chapter but to have guided learning path we have listed the various tasks
which we would be taking into care in this section of oracle for
beginners.
As part of the process flow starting from scratch
the below steps needs to be performed
- Step 1 :
Creation of responsibilities
- Step 2 :
Creation of user
- Step 3 : 4
Cs
- 3.1 : 1st C : Currency
- 3.2 : 2nd C : Calendar
- 3.3 : 3rd C : COA ( Accounting Flex field)
- 3.4 : 4th C : Defining SLA Method
- Step 4 : Defining
of ledger and attaching the 4C defined in step 3
- Step 5 :
Defining of location
- Step 6 :
Defining of organization
- Step 7 : Attaching of profile
option
Each step is a concept and will be discussed in breadth in
different posts.
3.1 1st C: Chart of Accounts: Define Accounting Flex field
As mentioned above 1st
C in the structure is COA or chart of accounts.
In order to define the chart of accounts we need to define the
accounting flex field and it follows the below steps
Accounting Flex field
> Segments > Value Sets > Values
The above means we need
to follow the below steps
·
Step 1: Define Accounting Flex field
·
Step 2: Define Segments
·
Step 3 : Define Value sets
·
Step 4 : Assign value sets to the
segments
·
Step 5 : Assign flex field qualifiers
·
Step 6 : Compiling of flex fields
·
Step 7 : Defining of values
3.2 2nd C: Currency
As mentioned above the next step after defining of the chart of accounts is to define the currency in the application.
3.3 3rd C: Calendar
- Defining of calendar names
- Defining of calendar periods
- Defining of exchange rates for the currency defined earlier.
All the above mentioned steps have been explained in the attached document.
Chapter 2 : Defining of 4Cs in EBS
Chapter 2 : Defining of 4Cs in EBS
4 Conclusion
Thus in today’s chapter we have studied the following
things
- · Multi-org Structure
- · Defining of 4Cs i.e.
ü
COA:
Accounting Flex field consisting of segments, Value sets, Values
ü
Calendar:
calendar name and periods
ü
Currency
:
ü
4th
C: SLA which being a vast topic would be taken up in a different session.
In our process we would attach the standard oracle defined SLA and end the process.
In our process we would attach the standard oracle defined SLA and end the process.
The steps mentioned in this chapter have
been explained considering the training requirements which would differ in case
of specific requirements. Next we would be seeing the process of defining of
ledgers and then assigning of the 4Cs to the ledger.